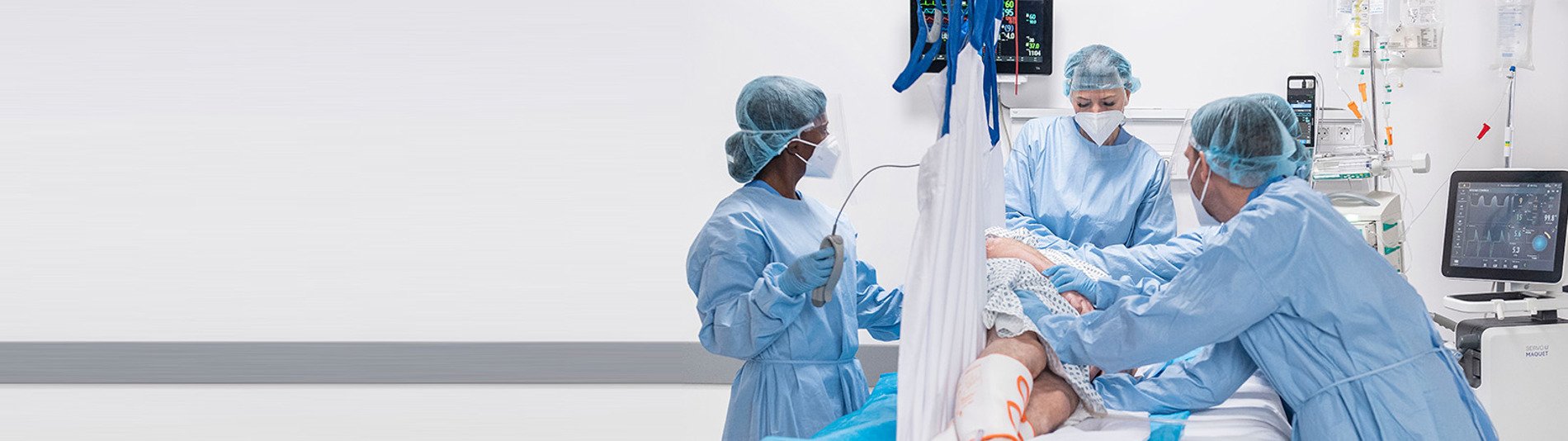
Arjo製品を利用した腹臥位は:
1. 筋骨格系の負傷リスクを低減し、ケア効率を向上させます
ペイシェントハンドリングソリューションは、介助者の怪我のリスクを低減し、腹臥位の効果を促進します¹、²:
- 身体的負荷の軽減
- 必要とされる介助者数の削減
- 介助者は制御された手法で操縦を行うことができます
2. 安全で制御された手法で患者様の体位変換を可能にします
患者様の体位変換の支援にリフトを使用します:
- 操作性に優れ、安全で優しい体位変換を実現します
- 体位変換時の有害事象リスクの低減にも役立つことがあります
3. 圧力損傷予防
患者様は1日16時間を超える長時間を腹臥位で過ごすことが多く³、圧力損傷予防はこれまでになく重要となっています。
適切なサポート面の使用による圧力再分配、マイクロクライメイト管理、およびその他の治療機能は、重要な介入です。
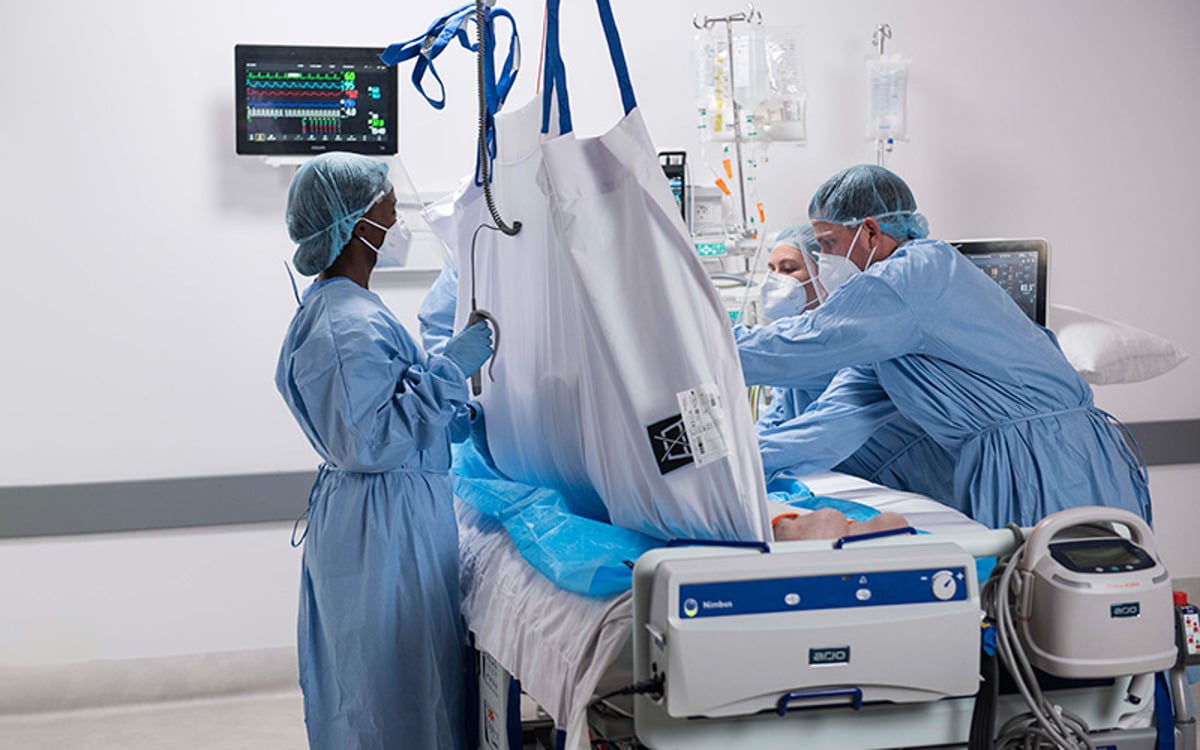
うつ伏せ/仰向けへの体位変換
Prone positioning involves turning a patient onto their chest. This may sound like a straightforward task. However, clinicians appreciate that this can be a complex, labour intensive manoeuvre that can put both patients and caregivers at risk.
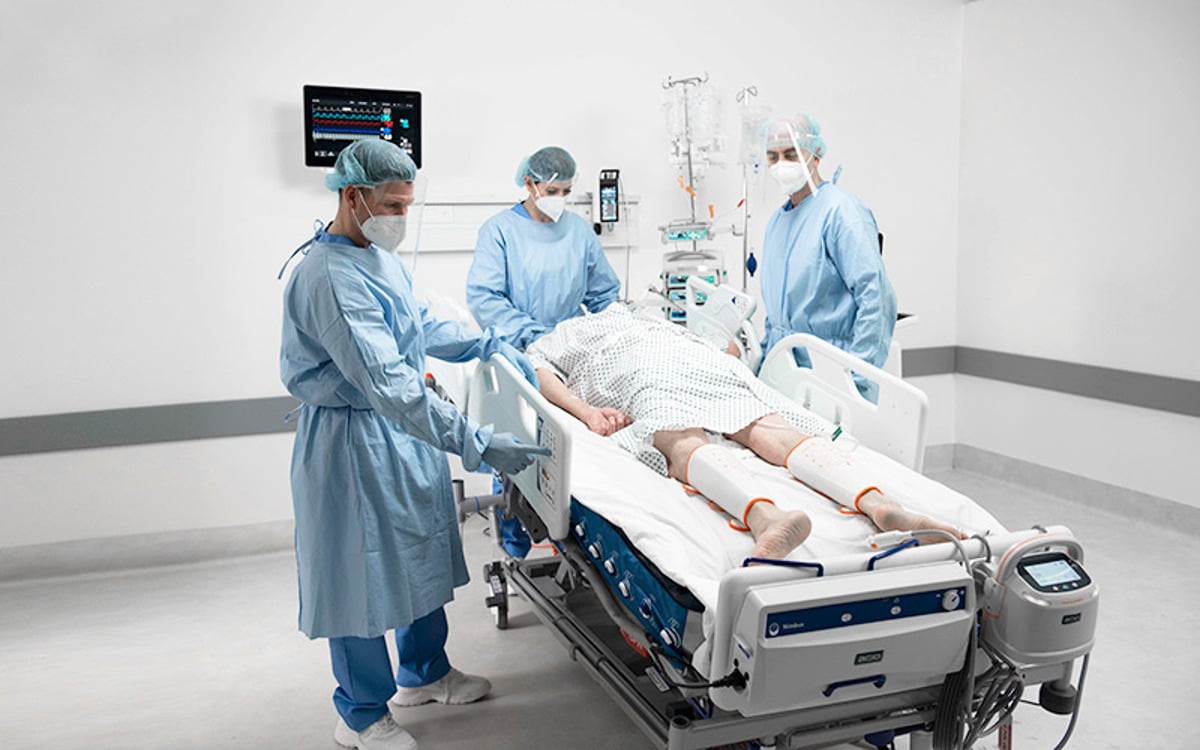
腹臥位
Patients often spend up to 16 hours out of every 24-hour period in the prone position⁴. Such lengthy sessions are associated with an increased risk of pressure injury.⁵
参考文献
- Latvala, S. and Masterman, R. 2020. The Evolution of the Ceiling Lift: A Glimpse at How a Single Device Has Redefined Caregiver Safety and Patient Care. International Journal of Safe Patient Handling and Mobility, 10(3).
- Church, M. and Chechile, J. 2020. Evaluation of Techniques for Prone Positioning Using Safe Patient Handling Equipment. International Journal of Safe Patient Handling and Mobility, 10(3).
- Papazian, L., Aubron, C., Brochard, L., Chiche, J., Combes, A., Dreyfuss, D., Forel, J., Guérin, C., Jaber, S., Mekontso-Dessap, A., Mercat, A., Richard, J., Roux, D., Vieillard-Baron, A. and Faure, H., 2019. Formal guidelines: management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Annals of Intensive Care, 9(1).
- Guerin C, et al, 2013. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med.
- Girard R, Baboi L, et al., 2014. The impact of patient positioning on pressure ulcers in patients with severe ARDS: results from a multicentre randomised controlled trial on prone positioning. Intensive Care Med.